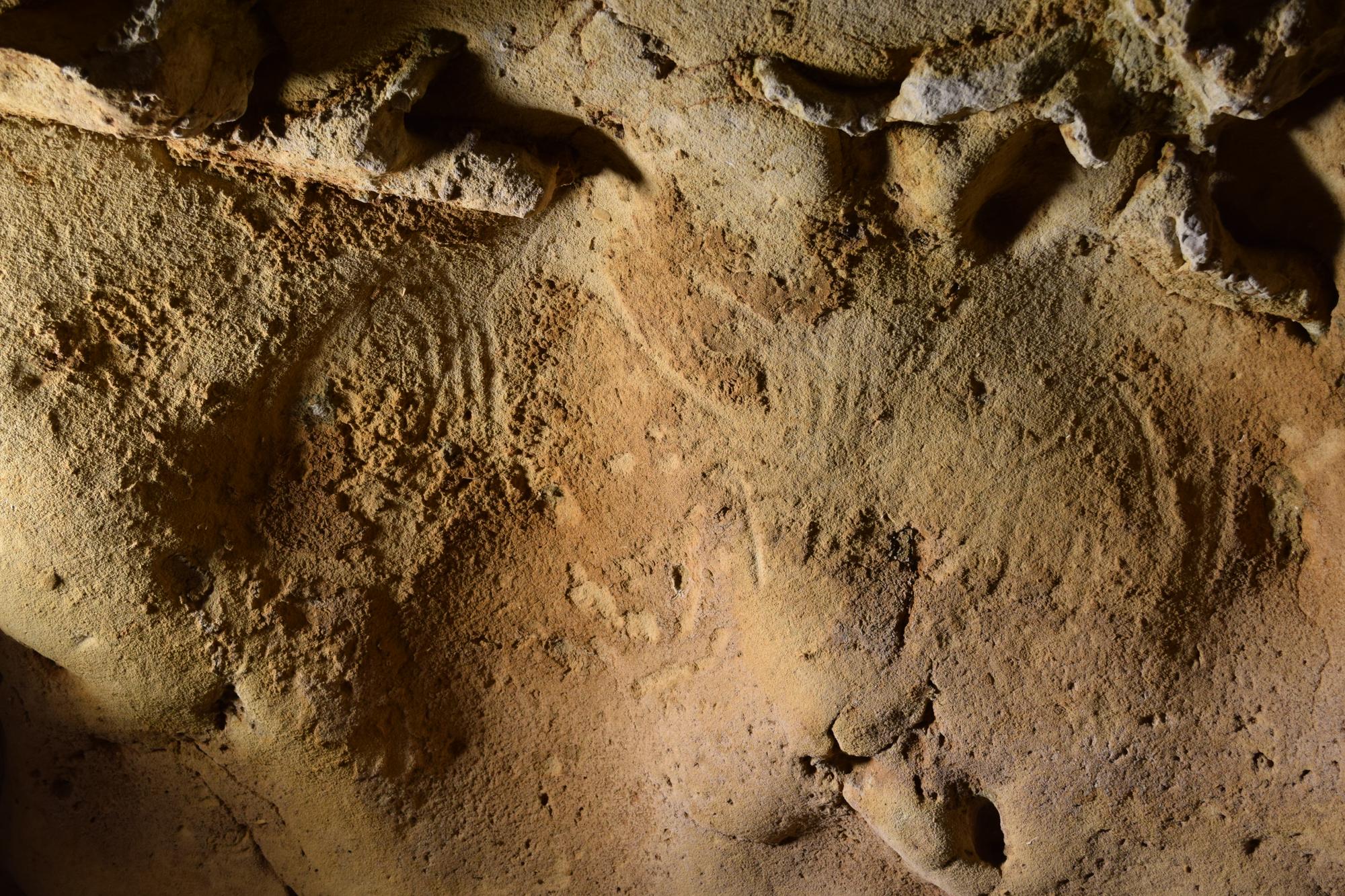
| Chère lectrice, cher lecteur, Patient aux HUG atteint d'une infection pulmonaire chronique causée par une bactérie multirésistante, José-Maria Vidal était agonisant, branché 24h/24 sur une perfusion d'antibiotiques à défaut de quoi il risquait de s'étouffer dans ses sécrétions. Il a songé à en finir. Son médecin lui a proposé une thérapie non encore homologuée en Suisse, la phagothérapie, c'est-à-dire à base de phages qui sont des virus tueurs de bactéries. Après quelques jours, l'atteinte pulmonaire disparaît. Notre collègue Sylvie Logean a pu parler à José-Maria et elle raconte son histoire dans le Temps. Son cas permettra-t-il aux autorités sanitaires d'accélérer l'homologation de la phagothérapie? Ses médecins l'espèrent. La phagothérapie est pratiquée de nos jours dans des pays d'Europe de l'Est, mais délaissée depuis les années 60 en Occident. Il reste encore du chemin avant de la voir administrer plus largement. Bonne lecture!  | – Aurélie Coulon | | #01  Aux HUG, à l'article de la mort, il guérit grâce à des virus tueurs de bactéries Aux HUG, à l'article de la mort, il guérit grâce à des virus tueurs de bactéries Atteint d'une infection chronique résistante aux antibiotiques, José-Maria Vidal a été sauvé par des bactériophages aux Hôpitaux universitaires de Genève. Son cas fait l'objet d'une étude dans la revue «Nature Communications». Le traitement, lui, n'est toujours pas homologué par les agences réglementaires | #02  Les plus anciennes «gravures» rupestres attribuées à Néandertal décrites en France Les plus anciennes «gravures» rupestres attribuées à Néandertal décrites en France Des Néandertaliens auraient réalisé des tracés pariétaux avec les doigts, il y a plus de 57 000 ans, dans la grotte française de la Roche-Cotard, avant l'arrivée d'Homo sapiens dans la région | #03  L'endométriose aurait-elle une origine bactérienne? L'endométriose aurait-elle une origine bactérienne? Une étude japonaise suggère que la présence dans l'utérus de certaines bactéries pourrait contribuer au développement de cette pathologie gynécologique invalidante. Une découverte qui offre de nouvelles pistes thérapeutiques | #04  Comment boire son café sans arrière-goût amer pour le climat Comment boire son café sans arrière-goût amer pour le climat Votre carburant quotidien figure parmi les produits alimentaires ayant le plus d'impact sur l'environnement. Il est pourtant possible d'alléger son bilan carbone. Nos explications et conseils pratiques | #05  Le télescope James Webb a trouvé le chaînon manquant de la chimie cosmique Le télescope James Webb a trouvé le chaînon manquant de la chimie cosmique Le JWST a découvert des traces de «methyl cation», une molécule cruciale pour la chimie organique, dans un disque protoplanétaire. C'est la première fois que cette substance est trouvée dans l'espace après des décennies de recherches | | |




![An international team of scientists have used data collected by the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope to detect a molecule known as the methyl cation (CH3+) for the first time, located in the protoplanetary disc surrounding a young star. They accomplished this feat with a cross-disciplinary expert analysis, including key input from laboratory spectroscopists. The vital role of CH3+ in interstellar carbon chemistry has been predicted since the 1970s, but Webb's unique capabilities have finally made observing it possible — in a region of space where planets capable of accommodating life could eventually form. This image is NIRCam's view of the Orion Bar region studied by the team of astronomers. Bathed in harsh ultraviolet light from the stars of the Trapezium Cluster, it is an area of intense activity, with star formation and active astrochemistry. This made it a perfect place to study the exact impact that ultraviolet radiation has on the molecular makeup of the discs of gas and dust that surround new stars. The radiation erodes the nebula's gas and dust in a process known as photoevaporation; this creates the rich tapestry of cavities and filaments that fill the view. The radiation also ionises the molecules, causing them to emit light — not only does this create a beautiful vista, it also allows astronomers to study the molecules using the spectrum of their emitted light obtained with Webb's MIRI and NIRSpec instruments. The two very large, bright stars are two of the three stars in the θ² Orionis system — the Trapezium Cluster is also known as θ¹ Orionis. The brightest star here, θ² Orionis A, is surrounded by particularly bright and red puffs of dust, which are reflecting the star's light towards Earth. Its great brightness — it is visible with the naked eye — is due to the fact that θ² Orionis A is itself a ternary system made of three closely bound bright stars. There are more proplyds visible in this image than just d203-506 — the Orion Nebula is replete with such new stars. In the very top left, a tiny star is visible within a long, dusty cocoon. This globule has formed from the star's protoplanetary disc, as the disc is broken down by the energetic radiation of the Trapezium Cluster. Around the globule, a round shockwave is strikingly visible moving through the gas of the Orion Nebula. [Image description: A nebula made of many layers of cloudy, colourful material. The top-left side of the image is brightly lit, filled with wispy, thin material in pale shades of pink and blue. A thick bar of denser, cloudier material crosses diagonally at the bottom right. It begins as orange and grows darker and sparser down to the corner. Two very bright stars, with very long diffraction spikes, lie in this sparse area.]](https://letemps-focus.sirius.press/2023/06/26/ac04e8d_1687792633521-the-orion-bar-region-nircam-image.jpg)




No comments:
Post a Comment
🤔